Joget on Azure Kubernetes Service
You can deploy, run, and scale Joget on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), a fully managed Kubernetes service offered by Microsoft Azure. This guide simplifies the complex tasks of container orchestration and provides scalable solutions for managing containerized applications across a cluster of machines. By leveraging AKS, you benefit from automatic updates, integrated monitoring, and scaling without the need to deeply understand the intricacies of Kubernetes management. With AKS handling your infrastructure, the focus can completely shift towards improving application development and operations.
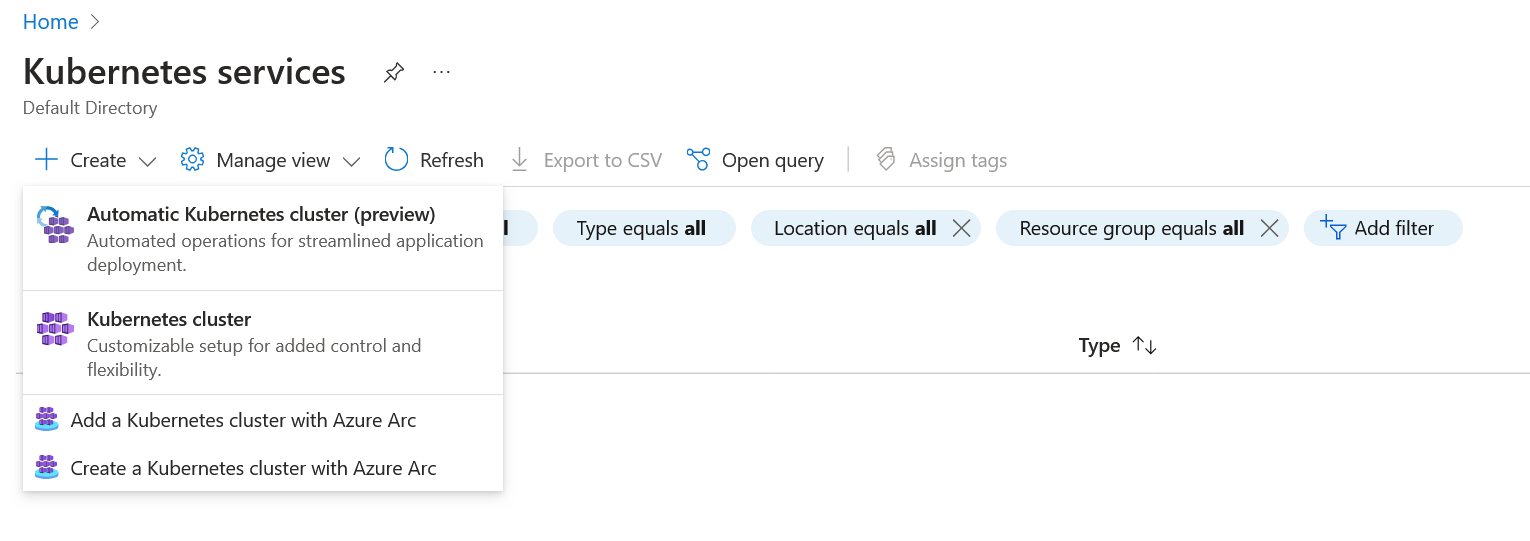
Create a kubernetes cluster in AKS
Using the Azure Portal:
-
Go to Kubernetes services and select Create a Kubernetes cluster.
-
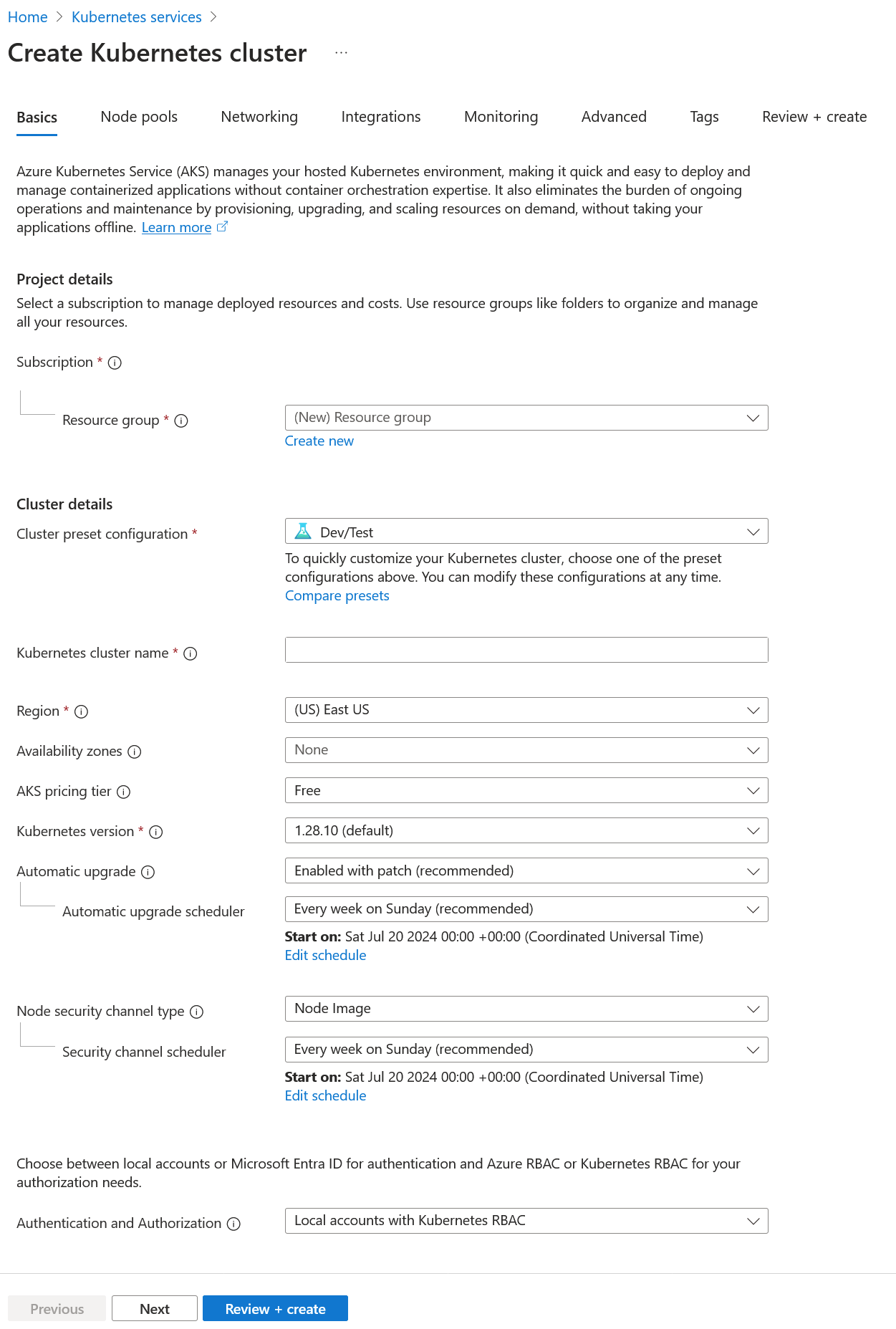
On the Basics tab, set your Subscription, Resource Group, and enter a Kubernetes cluster name. Adjust other configurations as needed.
-
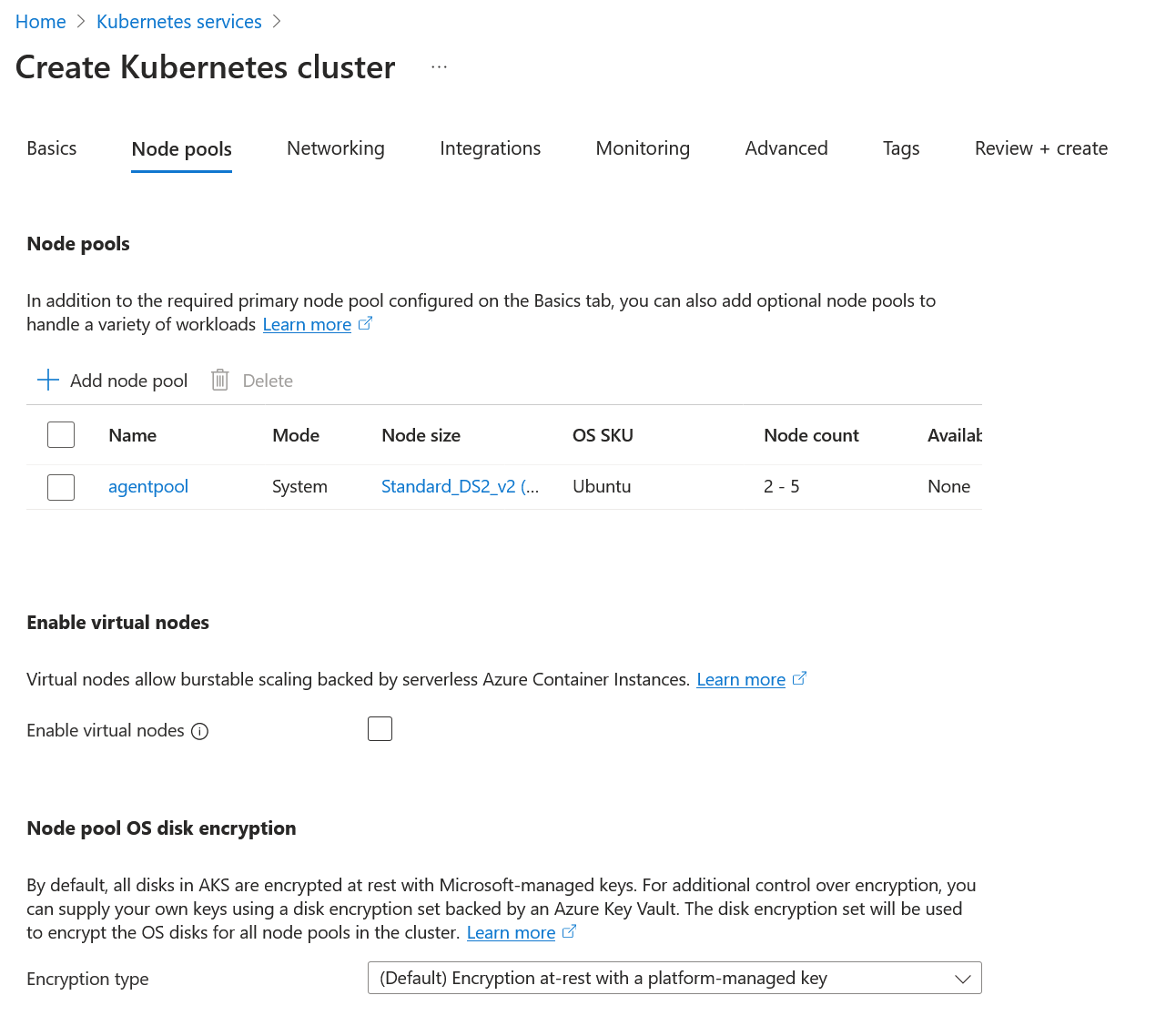
In the Node pools tab, configure the node pools. For more information, see Create node pools for a cluster in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
This guide assumes a single node configuration.
-
Leave default settings or make adjustments in the Access, Networking, Integrations, Advanced, and Tags tabs.
-
Click Review + create to deploy your Kubernetes cluster.
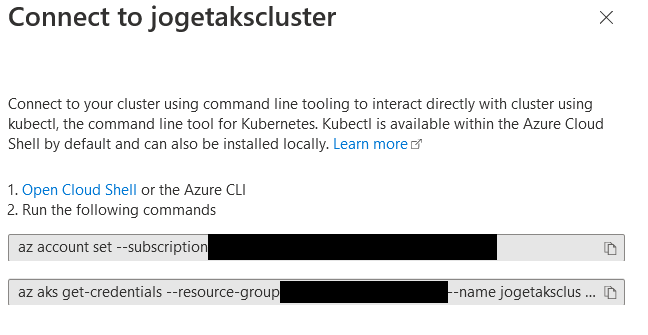
- After deployment, connect to your cluster using Azure CLI or Azure Cloud Shell. Learn how to connect.
Deploy MySQL database
Set up a MySQL database to support the Joget platform:
Apply the following example YAML files below to deploy the Persistent Volume (PV), Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) and MySQL database to the Kubernetes cluster
- Create persistent storage using
PersistentVolumeandPersistentVolumeClaiminmysql-pv.yaml: - Deploy the
mysql-pv.yamlfile
- Create the mysql-deployment.yaml
- Deploy the MySQL image:
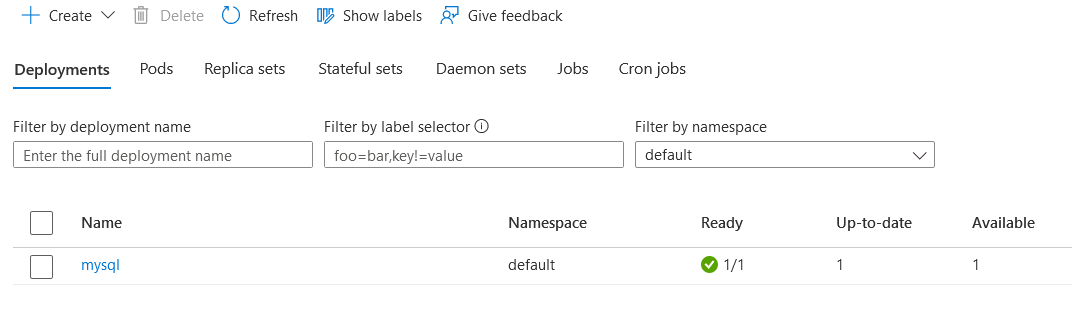
- Inspect the deployment:
Modify the original YAML files for production use, such as using a different MySQL image version and setting up secrets instead of plain passwords.
Deploy shared storage in AKS
For multi-node Kubernetes clusters, allocate shared persistent storage accessible by multiple nodes:
-
Create an Azure Ubuntu VM in the same virtual network as the AKS cluster.
-
Set up an NFS server on the VM using this script, modifying variables as necessary:
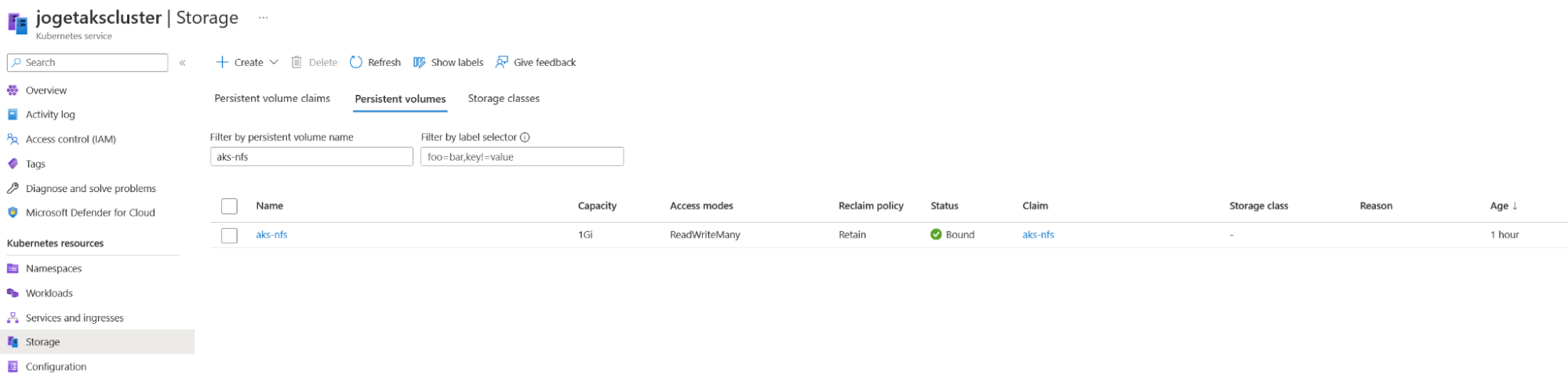
- Configure PersistentVolumes, apply the
azurenfsstorage.yamlfile, adjusting NFS settings as needed:
Update NFS Server Settings
Before applying the azurenfsstorage.yaml file, ensure that the values for NFS_INTERNAL_IP, NFS_NAME, and NFS_EXPORT_FILE_PATH are replaced with the actual settings from your NFS Server:
Deploy Joget DX
- With the necessary database and persistent storage configured, proceed to deploy Joget DX. Apply the
joget-dx8-tomcat9-aks.yamlfile to start the deployment process:
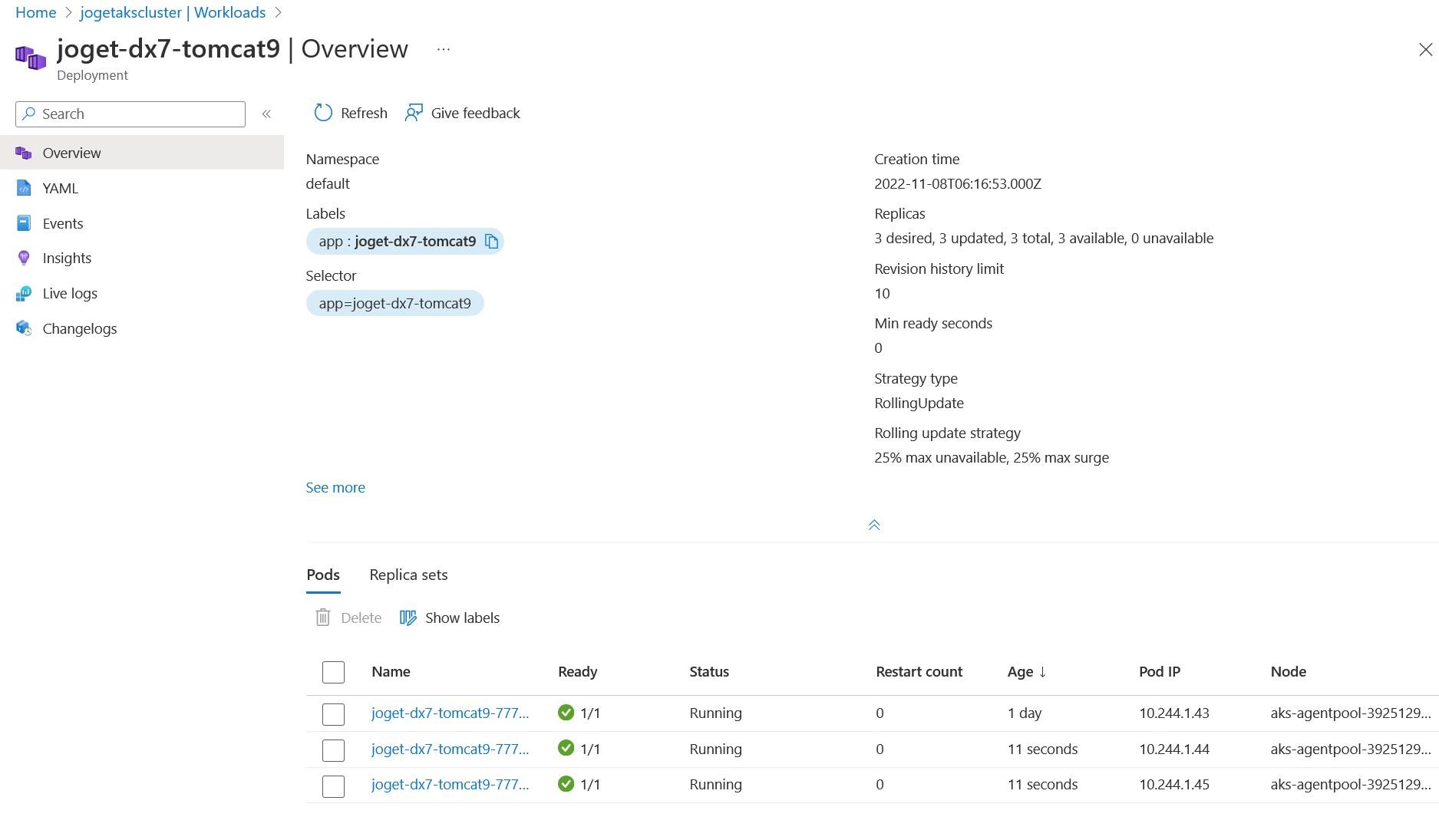
- You can monitor the deployment progress either from the Azure portal or by using Kubernetes commands, such as:
Deploy ingress for external connections
- Configure the Nginx Ingress Controller to enable external access to the Joget application. You can read more regarding Ingress in Kubernetes here. You can deploy it using Helm or from the Nginx Ingress Controller GitHub repository.
-
- Deploy Nginx Ingress Controller to AKS Cluster
You can refer to the AKS documentation regarding creating ingress-nginx and also the nginx-ingress document. -
Install using Helm:
Use Azure CLI/Cloud shell, set up the Helm for Nginx Ingress
- Deploy Nginx Ingress Controller to AKS Cluster
- After deploying the Ingress Controller, apply the
joget-ingress.yamlfile to enable external access:
Example thejoget-ingress.yaml:
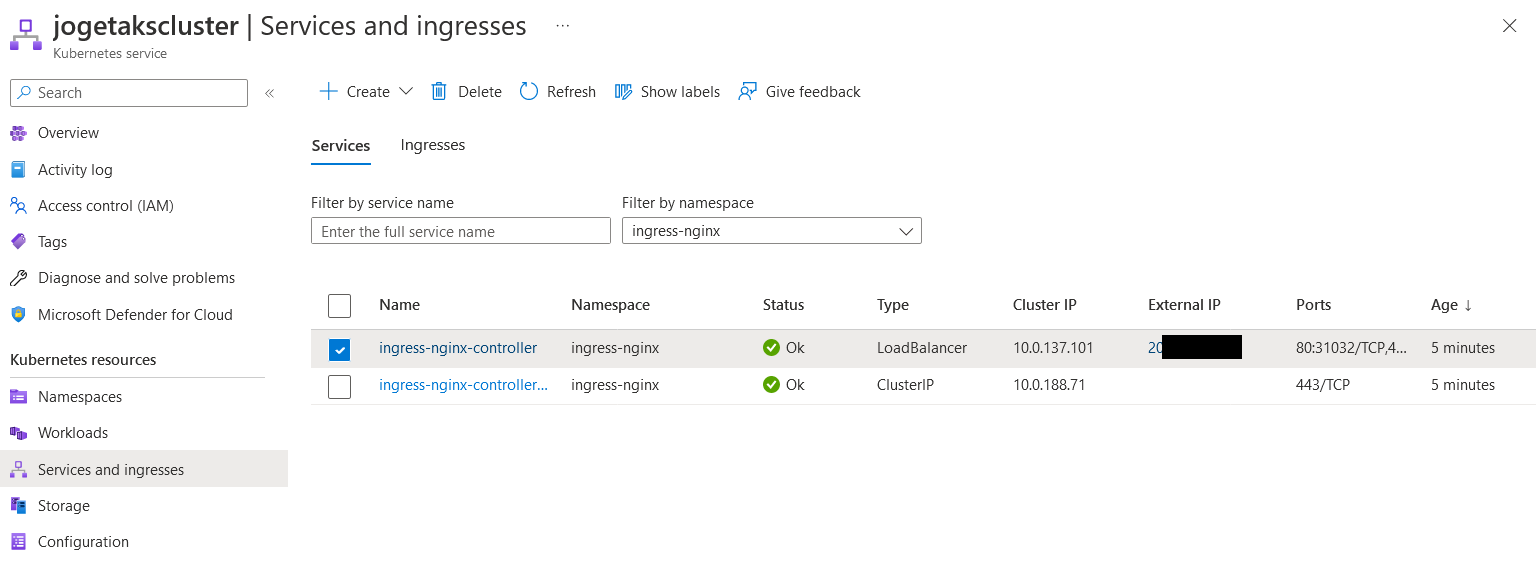
- Obtain the public IP address from the Kubernetes resources to access the application externally:
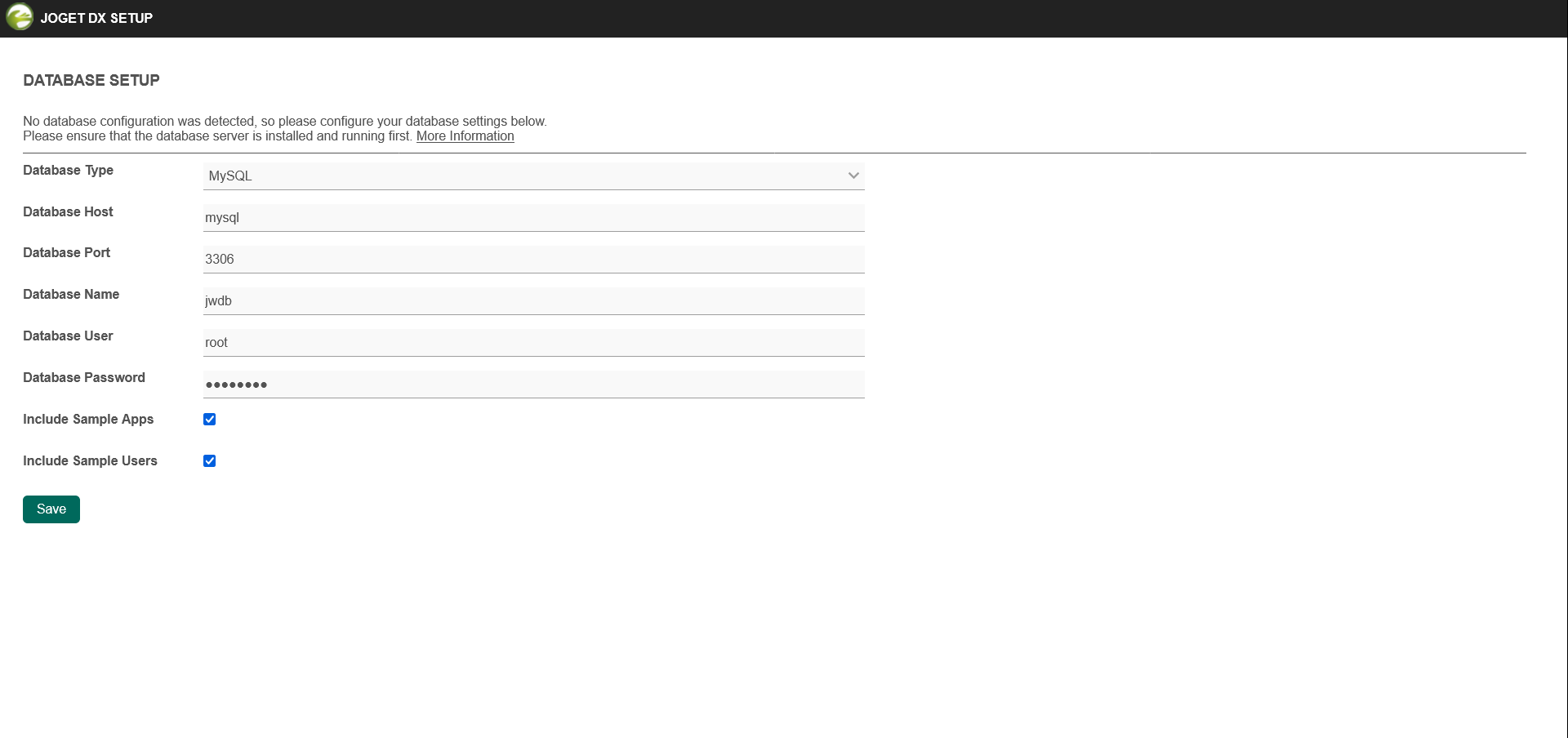
Database set up for Joget deployment
- Complete the database setup for Joget DX by entering the MySQL service name, database username, and password.
- Click Save.
-
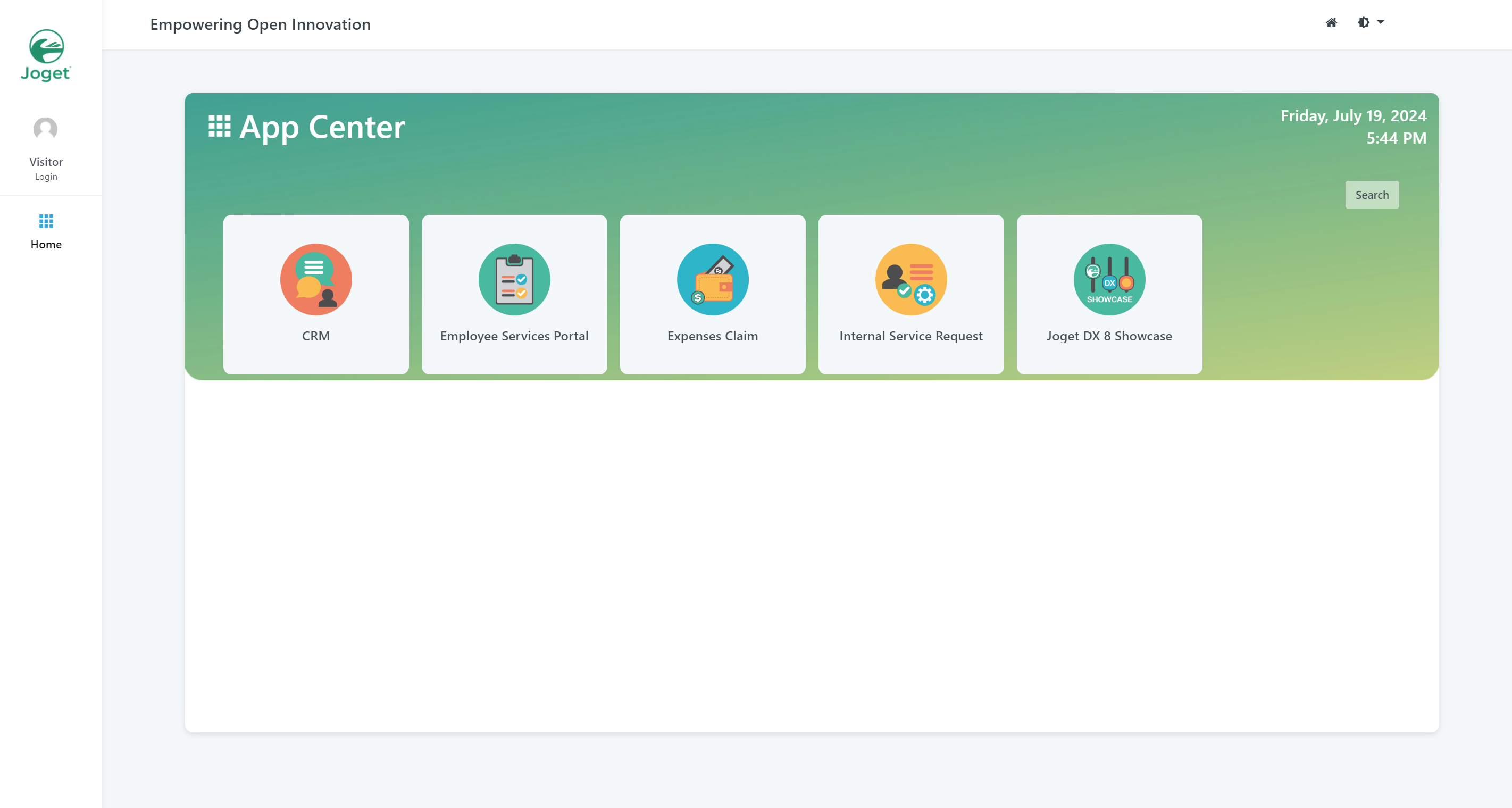
Once the set up is complete, click Done and you will be brought to the Joget App Center.
Set up cert-manager for TLS termination
Implementing TLS termination ensures secure communication by encrypting data in transit. To set up Cert-Manager for TLS termination in your Kubernetes cluster, follow these steps:
- Modify the Ingress configuration to support underscores in headers and enable snippet annotations. Create or update a ConfigMap (
ingress-configmap.yaml) with the following settings:Apply the updated configuration:
Install cert-manager into the cluster
- Install Cert-Manager in your cluster to manage the lifecycle of TLS certificates. You can install it using a YAML file from the official repository:
- Configure a ClusterIssuer to use Let's Encrypt for generating TLS certificates. Update the
stagingissuer.yamlfile with your details:
- Apply the issuer configuration:
- After deploying the issuer, check its status to ensure it is configured correctly:
Deploy/Update the Ingress with TLS Configuration
- Once deployed the Ingress without TLS configuration, update the Ingress yaml file to include the TLS configuration.
Example Ingress yaml with TLS: - This staging procedure ensures the certificate is generated correctly before setting up the Issuer with Let’s Encrypt production.
- Run the following command to get the current status of the certificates:
- The output of the command would be something similar to the following:
- Run the following command to get more details about the specific certificate:
- Once the certificate is generated correctly, set up the production Issuer. Below is an example
productionissuer.yamlfile:
- Update the ingress yaml file with the production annotation.
- Once updated the ingress yaml file, delete the previous secret to allow the new certifiate to be generated for production
- Run the describe command to check on the certificate status:
- Once the new certificate has been issued, access the Joget domain with HTTPS to ensure that it working as intended.
Scale deployment
Scaling your deployment effectively responds to changes in demand or capacity. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) supports both automatic and manual scaling methods.
Scale pods automatically
To scale the pods automatically in AKS, read here
Scale pods manually
To manually increase or decrease the number of pods running the Joget application, use the kubectl scale command. For example, to scale to three replicas:
Set the --replicas value to your desired number of pods, and the system will initialize and start up the pods accordingly.
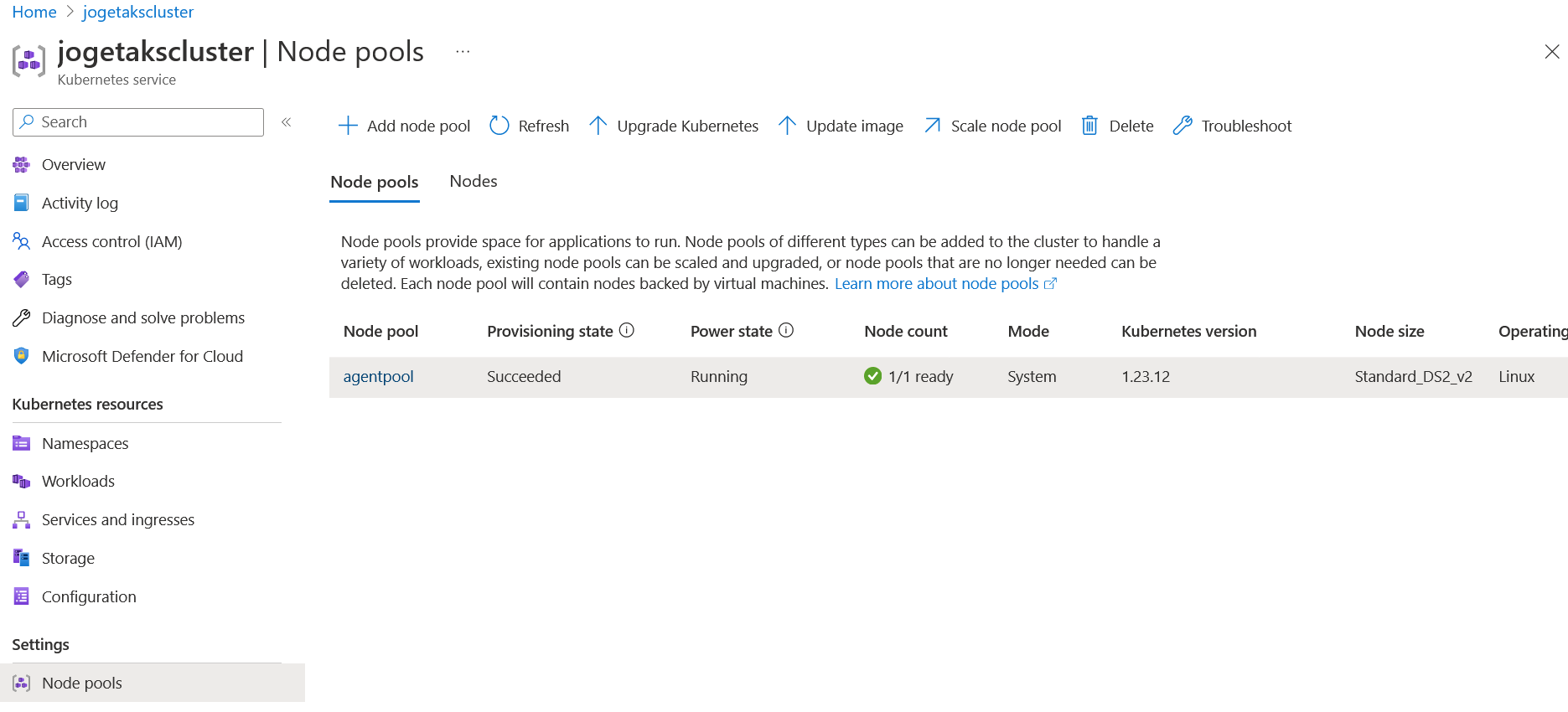
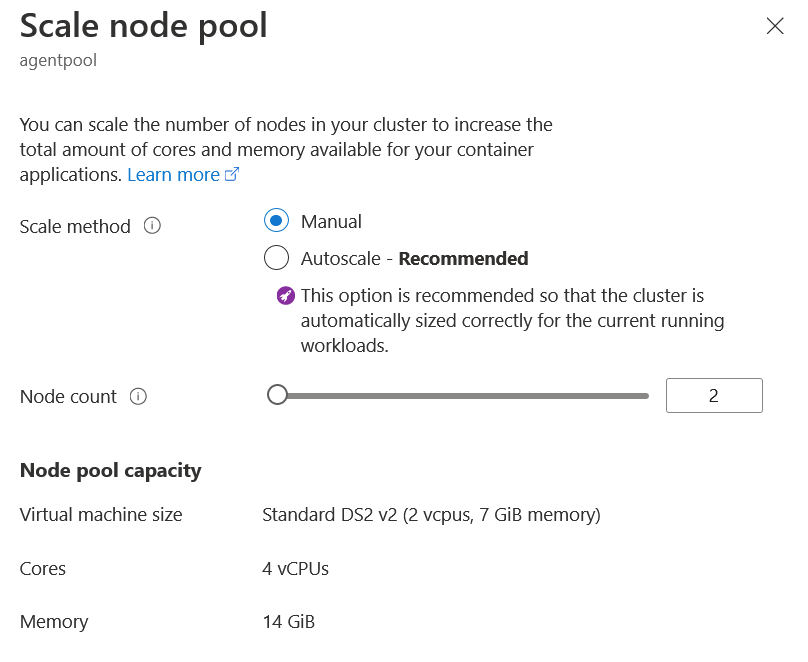
Scale nodes manually
Modify Node Count in the Azure Portal to adjust the number of nodes in your cluster: